Intro to Brain Computer Interface
مقدمة عن واجهة الدماغ الحاسوب
In this module you will learn the basics of Brain Computer Interface. You will read an introduction to the different technologies available, the main components and steps required for BCI, the safety and ethical issues and an overview about the future of the field.
في هذه الوحدة سوف تتعلم أساسيات واجهة الدماغ الحاسوبية. سوف تقرأ مقدمة للتقنيات المختلفة المتاحة ، والمكونات والخطوات الرئيسية المطلوبة لـ (همس) ، وقضايا السلامة والأخلاق ونظرة عامة حول مستقبل هذا المجال.
What is the definition
ما هو التعريف
Brain-computer interfaces (BCI) are systems that allow communication between the brain and various machines. They work in three main steps: collecting brain signals, interpreting them and outputting commands to a connected machine according to the brain signal received. BCI can be applied to a variety of tasks, including but not limited to neurofeedback, restoring motor function to paralyzed patients, allowing communication with locked in patients and improving sensory processing. BCI can be separated in three categories depending on the method used to collect brain signals.
واجهات الدماغ والحاسوب (همس) هي أنظمة تسمح بالاتصال بين الدماغ والآلات المختلفة. إنهم يعملون في ثلاث خطوات رئيسية: جمع إشارات الدماغ وتفسيرها وإخراج الأوامر إلى جهاز متصل وفقًا لإشارة الدماغ المستلمة. يمكن تطبيق (همس) على مجموعة متنوعة من المهام ، بما في ذلك على سبيل المثال لا الحصر الارتجاع العصبي ، واستعادة الوظيفة الحركية للمرضى المشلولين ، والسماح بالتواصل مع المرضى المحبوسين وتحسين المعالجة الحسية. يمكن فصل (همس) إلى ثلاث فئات اعتمادًا على الطريقة المستخدمة لجمع إشارات الدماغ.
What are the types of BCI’s
ما هي أنواع (همس)
There are many different techniques to measure brain signals. We can divide them into Non-Invasive, Semi-invasive and Invasive.
هناك العديد من التقنيات المختلفة لقياس إشارات الدماغ. يمكننا تقسيمها إلى غير غازية وشبه جائرة وجائرة.
Non-invasive
غير جراحي
The sensors are placed on the scalp to measure the electrical potentials produced by the brain (EEG) or the magnetic field (MEG).
توضع المستشعرات على فروة الرأس لقياس الجهود الكهربائية التي ينتجها الدماغ (EEG) أو المجال المغناطيسي (MEG)

Semi-invasive
شبه جراحيه
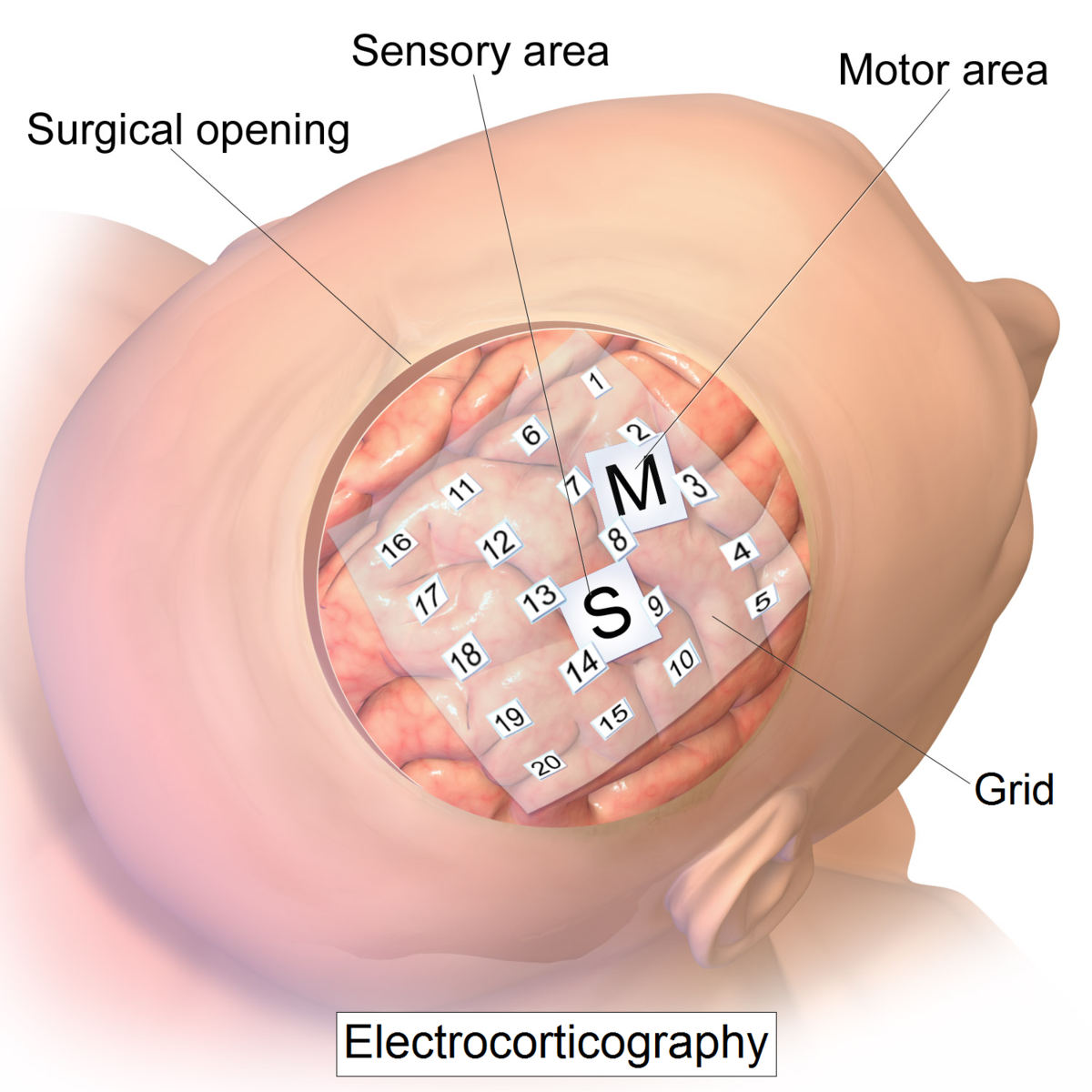
The electrodes are placed on the exposed surface of the brain(ECoG).
يتم وضع الأقطاب الكهربائية على السطح المكشوف للدماغ (ECoG).
Invasive
جراحيه بشكل كامل
The micro-electrodes are placed directly into the cortex, measuring the activity of a single neuron.
يتم وضع الأقطاب الكهربائية الدقيقة مباشرة في القشرة ، لقياس نشاط خلية عصبية واحدة.
The following image shows the different layers of the brain and where the signal is taken from.
تُظهر الصورة التالية طبقات الدماغ المختلفة ومن أين يتم أخذ الإشارة.
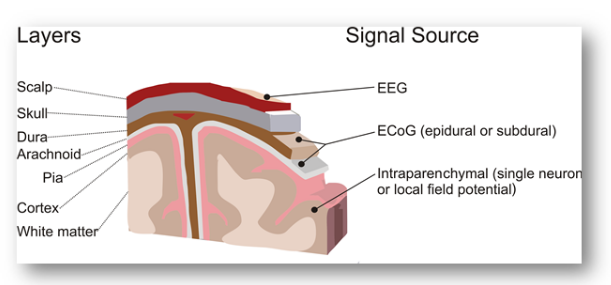
Non-invasive: the EEG signal is taken placing electrodes on the scalp, so on the most external part.
غير جراحي: يتم أخذ إشارة التخطيط الدماغي بوضع أقطاب كهربائية على فروة الرأس ، وهكذا في الجزء الخارجي.
Semi-invasive: the ECoG signal is taken from electrodes placed in the dura or in the arachnoid.
شبه جراحي: تُؤخذ إشارة ECoG من أقطاب كهربائية موضوعة في الجافية أو في العنكبوتية.
Invasive: the Intraparenchymal signal is taken directly implanting electrodes in the cortex.
جراحي: تؤخذ إشارة intraparenchymal مباشرة لزرع أقطاب كهربائية في القشرة.
Invasive
جراحي
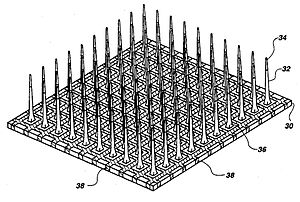
Invasive types of BCI are implanted directly into the brain during a neurosurgery. There are single unit BCIs, which detect the signal from a single area of brain cells, and multiunit BCIs which detect from multiple areas. Electrodes have different lengths, for example, up to 1.5 mm (Utah, Blackrock Microsystems) or 10 mm (FMA, MicroProbes) in a MEA (1) . The quality of the signal is the highest, but the procedure has several problematics, as for example the risk of forming scar tissues. The body reacts to the foreign object and builds the scar around the electrodes, which cause deterioration in the signal. Because neurosurgery can be a risky and expensive process, the target of invasive BCI are mainly blind and paralyzed patients.
يتم زرع الأنواع الجراحيه من (همس) مباشرة في الدماغ أثناء جراحة المخ والأعصاب. هناك وحدة واحدة (همس) ، والتي تكتشف الإشارة من منطقة واحدة من خلايا الدماغ ، و (همس) متعددة الوحدات التي تكتشف من مناطق متعددة. الأقطاب الكهربائية لها أطوال مختلفة ، على سبيل المثال ، تصل إلى 1.5 مم (يوتا ، Blackrock Microsystems) أو 10 مم (FMA ، MicroProbes) في منطقة الشرق الأوسط وأفريقيا (1). جودة الإشارة هي الأعلى ، لكن الإجراء به العديد من المشاكل ، على سبيل المثال خطر تكوين أنسجة ندبة. يتفاعل الجسم مع الجسم الغريب ويبني الندبة حول الأقطاب الكهربائية ، مما يتسبب في تدهور الإشارة. نظرًا لأن جراحة الأعصاب يمكن أن تكون عملية محفوفة بالمخاطر ومكلفة ، فإن هدف (همس) الغازي هو بشكل أساسي المرضى المكفوفين والمصابين بالشلل.
Semi-Invasive
شبه جراحيه
ECoG
تخطيط كهرباوي قشري
Electrocorticography uses electrodes placed on the exposed surface of the brain to measure electrical activity from the cerebral cortex. It has been used for the first time in the 1950s at the Montreal Neurological Institute. It is called semi-invasive but it still requires a craniotomy to implant the electrodes. For this reason it is used only when surgery is necessary for medical reasons (epilepsy for example).
يستخدم تخطيط كهربية القشرة أقطابًا كهربائية موضوعة على السطح المكشوف للدماغ لقياس النشاط الكهربائي من القشرة الدماغية. تم استخدامه لأول مرة في الخمسينيات من القرن الماضي في معهد مونتريال للأعصاب. يطلق عليه شبه الغازية ولكنه لا يزال يتطلب حج القحف لزرع الأقطاب الكهربائية. لهذا السبب يتم استخدامه فقط عندما تكون الجراحة ضرورية لأسباب طبية (الصرع على سبيل المثال).
The electrodes may be placed outside the dura mater (epidural) or under the dura mater (subdural). The strip or grid electrodes covers a large area of the cortex (from 4 to 256 electrodes)(2), allowing a diverse range of cognitive studies.
يمكن وضع الأقطاب الكهربائية خارج الجافية (فوق الجافية) أو تحت الأم الجافية (تحت الجافية). يغطي الشريط أو الأقطاب الشبكية مساحة كبيرة من القشرة (من 4 إلى 256 قطبًا كهربائيًا) (2) ، مما يسمح بمجموعة متنوعة من الدراسات المعرفية.
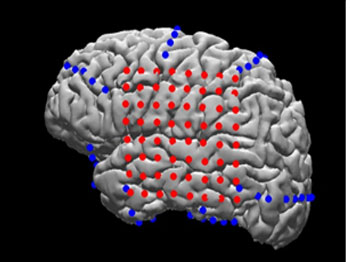
In the image: MRI reconstruction of the patient’s brain with electrodes overlaid (red: grid array; blue: strip arrays) to allow precise matching of neurophysiological activity to neuroanatomical structures (Image from: Yang et al., Neuroimage, 2012)
في الصورة: إعادة بناء دماغ المريض بواسطة التصوير بالرنين المغناطيسي باستخدام أقطاب كهربائية متراكبة (أحمر: مصفوفة شبكية ؛ أزرق: مصفوفات شريطية) للسماح بمطابقة دقيقة للنشاط الفسيولوجي العصبي مع الهياكل التشريحية العصبية (صورة من: Yang et al.، Neuroimage، 2012)

The positive characteristics of ECoG are:
high spatial resolution and signal fidelity
resistance to noise
lower clinical risk and Robustness over long recording period[1]
higher amplitude
الخصائص الإيجابية لتخطيط كهرباوي قشري هي:
دقة مكانية عالية وإشارة إخلاص
مقاومة الضوضاء
انخفاض المخاطر السريرية والمتانة على مدى فترة تسجيل طويلة [1]
سعة أعلى
Spatial resolution
الدقة المكاني
A benefit of the ECoG over EEG, is that the spatial resolution is much higher because the signal doesn’t have to travel to reach the scalp. The spatial resolution in ECoG is tenths of millimeters, while it is centimeters in EEG (4).
تتمثل إحدى مزايا تخطيط كهرباوي قشري (ECoG) على مخطط كهربية الدماغ (EEG) في أن الدقة المكانية أعلى بكثير لأن الإشارة لا يجب أن تنتقل للوصول إلى فروة الرأس. تبلغ الدقة المكانية في ECoG أعشار المليمترات ، بينما تبلغ السنتيمترات في مخطط كهربية الدماغ (4).
What do we mean by spatial resolution? We can take, as an analogy, the clarity of an image. A picture with a higher spatial resolution is “clearer”; in other words, it looks more precise because it is composed of more pixels per inch, showing more details. A picture with lower spatial resolution appears less clear, or more blurry because it is composed of fewer pixels per inch. Better spatial resolution allows us to understand with better precision where the signal is coming from. In the case of EEG, when the electrical signal travels through the skull, it is attenuated due to the low conductivity of the bones.
ماذا نعني بالدقة المكانية؟ يمكننا أن نأخذ ، على سبيل القياس ، وضوح الصورة. تكون الصورة ذات الدقة المكانية الأعلى "أوضح" ؛ بمعنى آخر ، يبدو أكثر دقة لأنه يتكون من عدد أكبر من البكسل في البوصة ، مما يُظهر مزيدًا من التفاصيل. تظهر الصورة ذات الدقة المكانية المنخفضة أقل وضوحًا ، أو أكثر ضبابية لأنها تتكون من عدد أقل من وحدات البكسل في البوصة. تتيح لنا الدقة المكانية الأفضل أن نفهم بدقة أفضل من أين تأتي الإشارة. في حالة مخطط كهربية الدماغ ، عندما تنتقل الإشارة الكهربائية عبر الجمجمة ، يتم إضعافها بسبب التوصيل المنخفض للعظام.
Resistance to noise
مقاومة الضوضاء
ECoG signal is not impacted by noise and artifacts as for example EMG (electromyographic - caused by muscles movements) and EOG (electrooculographic - caused by eyes movements)
لا تتأثر إشارة تخطيط كهرباوي قشري بالضوضاء والتشوهات مثل مخطط كهربية العضل (تخطيط كهربية العضل - الناجم عن حركات العضلات) وتخطيط كهربية القلب (تخطيط كهربية القلب - الناجم عن حركات العين)
Lower clinical risk
مخاطر سريرية أقل
The electrode arrays doesn’t need to penetrate into the cortex, which makes it safer than invasive recording (4)
لا تحتاج مصفوفات الأقطاب إلى اختراق القشرة ، مما يجعلها أكثر أمانًا من التسجيل الغازي (4)
Higher amplitude
سعة أعلى
ECoG recordings are 50–100 µV maximum versus 10–20 µV
تسجيلات ECoG هي 50-100 ميكرو فولت كحد أقصى مقابل 10-20 ميكرو فولت
In BCI
في (همس)
There have been different studies about the use of ECoG in BCI, but they are all limited to cases where surgery was needed to remove an epileptic focus. In one study (5) for example, the researcher used ECoG to control a computer cursor in two dimensions. Five patients, in preparation of surgery for epilepsy, had a subdural array of electrodes implanted for 7-14 days. After a short training of less than 30 minutes, the patients have been able to control a cursor in two dimensions, with an average success rate of 53-73%.
كانت هناك دراسات مختلفة حول استخدام ECoG في (همس) ، لكنها تقتصر جميعها على الحالات التي تتطلب الجراحة لإزالة بؤرة الصرع. في دراسة واحدة (5) على سبيل المثال ، استخدم الباحث ECoG للتحكم في مؤشر الحاسوب في بعدين. خمسة مرضى ، استعدادًا لعملية جراحية للصرع ، تم زرع مجموعة من الأقطاب الكهربائية تحت الجافية لمدة 7-14 يومًا. بعد تدريب قصير مدته أقل من 30 دقيقة ، تمكن المرضى من التحكم في المؤشر في بعدين ، بمتوسط معدل نجاح 53-73٪.
Non Invasive
غير الجراحية
In the following section we will review briefly the main non-invasive techniques. There are several non-invasive techniques used to study the brain, where EEG is the most common used because of the cost and hardware portability.
في القسم التالي سوف نستعرض بإيجاز التقنيات الرئيسية غير الغازية. هناك العديد من التقنيات غير الغازية المستخدمة لدراسة الدماغ ، حيث يعتبر مخطط كهربية الدماغ هو الأكثر استخدامًا بسبب التكلفة وقابلية الأجهزة.
MEG magnetoencephalography
PET positron emission tomography
fMRI functional magnetic resonance imaging
fNIRS near-infrared spectroscopy
EEG Electroencephalography
تخطيط الدماغ المغناطيسي MEG
التصوير المقطعي بالإصدار البوزيتروني
التصوير بالرنين المغناطيسي الوظيفي
مطيافية الأشعة تحت الحمراء القريبة من الأشعة تحت الحمراء
تخطيط كهربية الدماغ
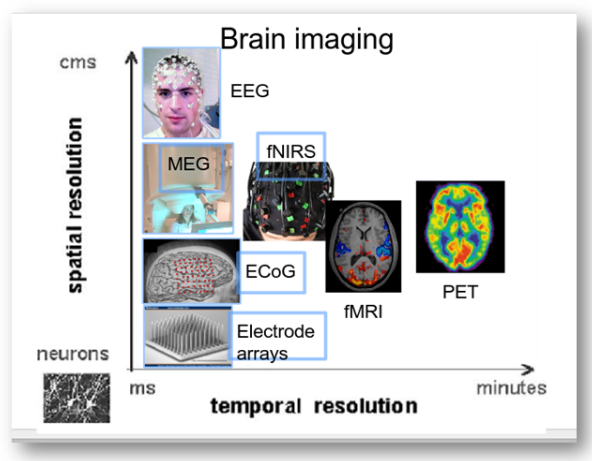
In the following image is possible to see the different brain imaging techniques, compared by spatial and temporal resolution:
في الصورة التالية من الممكن رؤية تقنيات تصوير الدماغ المختلفة ، مقارنة بالدقة المكانية والزمانية:
MEG magnetoencephalography
تخطيط الدماغ المغناطيسي
What is it? From Wikipedia “is a functional neuroimaging technique for mapping brain activity by recording magnetic fields produced by electrical currents occurring naturally in the brain, using very sensitive magnetometers.“
ما هذا؟ من ويكيبيديا "هي تقنية تصوير عصبي وظيفية لرسم خرائط لنشاط الدماغ عن طريق تسجيل المجالات المغناطيسية التي تنتجها التيارات الكهربائية التي تحدث بشكل طبيعي في الدماغ ، باستخدام مقاييس مغناطيسية حساسة للغاية.
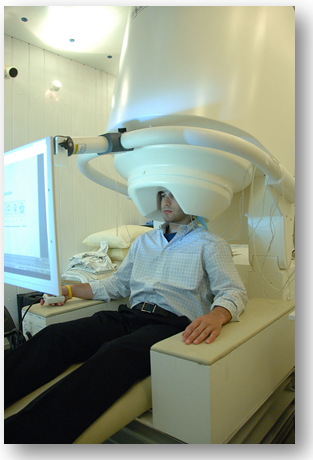
In the image: MEG scanner with patient from National Institute of Mental Health (6)
في الصورة: ماسح ضوئي MEG مع مريض من المعهد الوطني للصحة العقلية (6)
How does it work? MEG measures the magnetic field caused by the currents in the brain, and it offers a better spatial resolution compared to EEG (7). Why? Because magnetic fields suffer far less than electric fields from the spatial blurring effect of the skull and intracerebral fluid (8). “MEG is maximally sensitive to tangential sources and has low sensitivity to radial sources” “MEG is better than EEG at detecting high-frequency activity (e.g., above 60 Hz). This is because magnetic fields pass through the skull and scalp, whereas the electrical fields are volume conducted through these tissues, which decreases signal-to-noise ratio at higher frequencies.”
كيف يعمل؟ يقيس MEG المجال المغناطيسي الناجم عن التيارات في الدماغ ، ويوفر دقة مكانية أفضل مقارنةً بـ EEG (7). لماذا ا؟ لأن الحقول المغناطيسية تعاني أقل بكثير من المجالات الكهربائية من تأثير التشويش المكاني للجمجمة والسائل داخل المخ (8). "MEG حساس إلى أقصى حد للمصادر العرضية ولديه حساسية منخفضة للمصادر الشعاعية" "MEG أفضل من EEG في اكتشاف النشاط عالي التردد (على سبيل المثال ، أعلى من 60 هرتز). وذلك لأن الحقول المغناطيسية تمر عبر الجمجمة وفروة الرأس ، في حين أن الحقول الكهربائية يتم توصيلها بالحجم من خلال هذه الأنسجة ، مما يقلل نسبة الإشارة إلى الضوضاء عند الترددات الأعلى ".
PET positron emission tomography
التصوير المقطعي بالإصدار البوزيتروني
What is it? PET is a nuclear imaging technique used in medicine to observe different processes, such as blood flow, metabolism, neurotransmitters, happening in the body.
ما هذا؟ PET هي تقنية تصوير نووي تُستخدم في الطب لمراقبة العمليات المختلفة ، مثل تدفق الدم ، والتمثيل الغذائي ، والناقلات العصبية ، التي تحدث في الجسم.
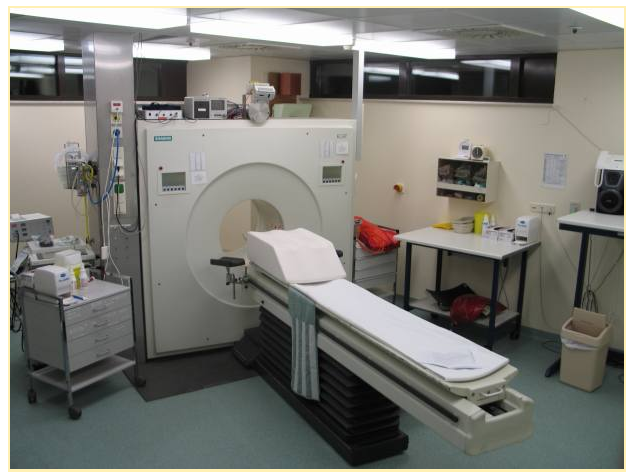
“This image shows a picture taken from a typical PET facility equipped with an ECAT Exact HR+ PET scanner. PET scanners such as this are steadily being replaced by systems that combine both PET and CT scanners into a single PET/CT imaging device.” (9)
"تُظهر هذه الصورة صورة مأخوذة من منشأة نموذجية للحيوانات الأليفة مزودة بجهاز فحص ECAT Exact HR + PET. يتم باستمرار استبدال ماسحات التصوير المقطعي بالإصدار البوزيتروني مثل هذه بأنظمة تجمع بين كل من ماسحات PET و CT في جهاز تصوير واحد PET / CT. " (9)
How does it work? A small amount of radioactive material, called radiotracer, is injected in the bloodstream to reach the brain. In the case of the brain, the radiotracer get attached to the glucose and creates a radionuclide called fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) (10). The brain uses glucose and it will show different levels based on the level activity of the different regions. The images of the PET scan are multicolored, where areas with more activities are in warmer colors as yellow and red. PET scans of the brain are used often to detect illnesses as cancer or others.
كيف يعمل؟ يتم حقن كمية صغيرة من المواد المشعة ، تسمى Radiotracer ، في مجرى الدم لتصل إلى الدماغ. في حالة الدماغ ، يتم ربط جهاز التتبع الإشعاعي بالجلوكوز ويخلق نويدات مشعة تسمى fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) (10). يستخدم الدماغ الجلوكوز وسيظهر مستويات مختلفة بناءً على مستوى نشاط المناطق المختلفة. صور فحص التصوير المقطعي بالإصدار البوزيتروني متعددة الألوان ، حيث تكون المناطق التي بها المزيد من الأنشطة بألوان أكثر دفئًا مثل الأصفر والأحمر. غالبًا ما تستخدم فحوصات التصوير المقطعي بالإصدار البوزيتروني للدماغ للكشف عن الأمراض مثل السرطان أو غيرها.
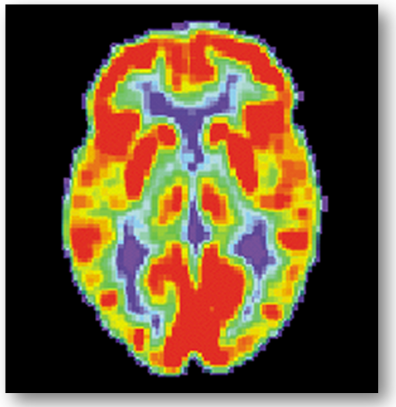
PET scan of a normal human brain
مسح PET لدماغ بشري طبيعي
fMRI functional magnetic resonance imaging
الرنين المغناطيسي الوظيفي
What is? Functional magnetic resonance imaging or functional MRI (fMRI) is a functional neuroimaging procedure using MRI technology that measures brain activity by detecting changes associated with blood flow.[1][2] This technique relies on the fact that cerebral blood flow and neuronal activation are coupled. When an area of the brain is in use, blood flow to that region also increases. (11)
التصوير بالرنين المغناطيسي الوظيفي أو التصوير بالرنين المغناطيسي الوظيفي (fMRI) هو إجراء وظيفي للتصوير العصبي باستخدام تقنية التصوير بالرنين المغناطيسي التي تقيس نشاط الدماغ عن طريق اكتشاف التغيرات المرتبطة بتدفق الدم. [1] [2] تعتمد هذه التقنية على حقيقة أن تدفق الدم في المخ وتنشيط الخلايا العصبية مرتبطان. عندما يتم استخدام منطقة من الدماغ ، يزداد أيضًا تدفق الدم إلى تلك المنطقة. (11)
fMRI has been developed in the 1990s. It is a non-invasive and safe technique, it doesn’t use radiation, it’s easy to use and it has excellent spatial and good temporal resolution. (12)
تم تطوير التصوير بالرنين المغناطيسي الوظيفي في التسعينيات. إنها تقنية غير جراحية وآمنة ، ولا تستخدم الإشعاع ، وهي سهلة الاستخدام وتتميز بدقة مكانية ممتازة ودقة زمنية جيدة. (12)
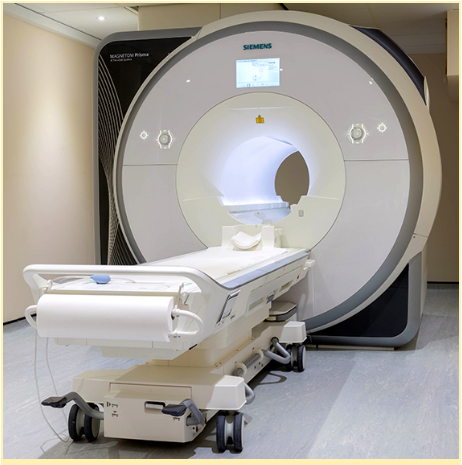
How does it work? In the brain, haemoglobin in capillary red blood cells delivers oxygen to the neurons. Activity causes more demand for oxygen, which leads to an increase of blood flow. The magnetic characteristics of haemoglobin change if it is or not oxygenated. This difference allows the MRI machine, which is a cylindrical tube with a powerful electro-magnet, to detect which areas of the brain are active in a specific moment.
كيف يعمل؟ في الدماغ ، يقوم الهيموغلوبين الموجود في خلايا الدم الحمراء الشعرية بتوصيل الأكسجين إلى الخلايا العصبية. يتسبب النشاط في زيادة الطلب على الأكسجين ، مما يؤدي إلى زيادة تدفق الدم. تتغير الخصائص المغناطيسية للهيموجلوبين إذا كان مؤكسجًا أم لا. يسمح هذا الاختلاف لجهاز التصوير بالرنين المغناطيسي ، وهو أنبوب أسطواني به مغناطيس كهربائي قوي ، باكتشاف مناطق الدماغ النشطة في لحظة معينة.
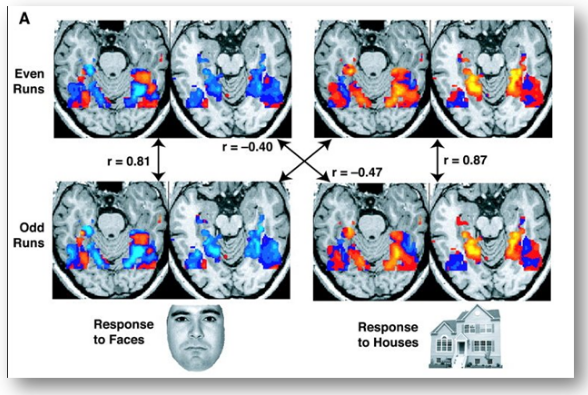
images from a study showing parts of the brain lighting up on seeing houses and other parts on seeing faces. The ‘r’ values are correlations, with higher positive or negative values indicating a better match.
صور من دراسة تظهر أجزاء من الدماغ تضيء عند رؤية المنازل وأجزاء أخرى عند رؤية الوجوه. القيم "r" هي ارتباطات ، حيث تشير القيم الإيجابية أو السلبية الأعلى إلى تطابق أفضل.
fNIRS near-infrared spectroscopy
مطيافية الأشعة تحت الحمراء القريبة من الأشعة تحت الحمراء
What is? Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy (fNIR or fNIRS), is the use of NIRS (near-infrared spectroscopy) for the purpose of functional neuroimaging. Using fNIR, brain activity is measured through hemodynamic responses associated with neuron behaviour. (13)
ما هو؟ التحليل الطيفي للأشعة تحت الحمراء القريبة (fNIR أو fNIRS) ، هو استخدام NIRS (التحليل الطيفي للأشعة تحت الحمراء القريبة) لغرض التصوير العصبي الوظيفي. باستخدام fNIR ، يتم قياس نشاط الدماغ من خلال الاستجابات الدورة الدموية المرتبطة بسلوك الخلايا العصبية. (13)
An optical technique to measure localized cortical brain activity (14)
How does it work? fNIRS measures the changes in blood flow as fMRI, but using a different technique, infrared light vs magnetic field.
تقنية بصرية لقياس نشاط الدماغ القشري الموضعي (14)
كيف يعمل؟ يقيس fNIRS التغيرات في تدفق الدم مثل التصوير بالرنين المغناطيسي الوظيفي ، ولكن باستخدام تقنية مختلفة ، ضوء الأشعة تحت الحمراء مقابل المجال المغناطيسي.
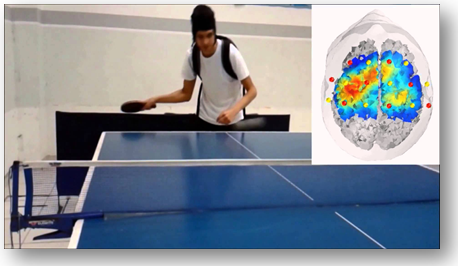
In the image: fNIRS during table-tennis experiment (15)
When a task begins there is consumption of oxygen, as the complexity increases, also the request for oxygen increases. fMRI measures how much oxygen is consumed. fNIRS measures also how much oxygen is available in the area (overshot).
Still, the temporal quality of fNIRS is not as good as EEG. fNIRS takes 10 samples per second, which is trumped by EEG’s 500 to 1000 samples per second. And the spatial resolution is not as good as fMRI. For example, fMRI can image subcortical brain regions, while fNIRS cannot analyze past the cortex, unable to capture any subcortical activation. Indeed, many researchers who presented their fNIRS at SfN are using the instrument as a supplement to their EEG or fMRI data. (16)
في الصورة: fNIRS أثناء تجربة تنس الطاولة (15)
عندما تبدأ المهمة ، هناك استهلاك للأكسجين ، مع زيادة التعقيد ، يزداد الطلب على الأكسجين أيضًا. يقيس الرنين المغناطيسي الوظيفي كمية الأكسجين المستهلكة. يقيس fNIRS أيضًا مقدار الأكسجين المتاح في المنطقة (تجاوز).
ومع ذلك ، فإن الجودة الزمنية لأشعة الأشعة تحت الحمراء ليست بجودة مخطط كهربية الدماغ. يأخذ fNIRS 10 عينات في الثانية ، وهو ما يتفوق عليه من 500 إلى 1000 عينة في الثانية من EEG. والدقة المكانية ليست بنفس جودة التصوير بالرنين المغناطيسي الوظيفي. على سبيل المثال ، يمكن للرنين المغناطيسي الوظيفي تصوير مناطق الدماغ تحت القشرية ، في حين أن fNIRS لا يمكنها تحليل ما وراء القشرة ، غير قادرة على التقاط أي تنشيط تحت القشرة. في الواقع ، يستخدم العديد من الباحثين الذين قدموا fNIRS في SfN الأداة كمكمل لبيانات EEG أو fMRI الخاصة بهم. (16)
Benefits:
Non-invasive
Portable
Accessible
Less sensible to artifacts compared to fMRI and EEG
فوائد:
غير جراحي
محمول
يمكن الوصول
أقل حساسية مقارنة بالرنين المغناطيسي الوظيفي ومخطط كهربية الدماغ
Has a temporal resolution more similar to EEG fMRI may record one sample per 2 seconds, fNIRS can record 10 samples per 1 second. (17) fNIRS better spatial resolution than EEG and better temporal resolution than fMRI
لديه دقة زمنية أكثر شبهاً بـ EEG fMRI قد يسجل عينة واحدة كل ثانيتين ، يمكن لـ fNIRS تسجيل 10 عينات في 1 ثانية. (17) fNIRS دقة مكانية أفضل من EEG ودقة زمنية أفضل من التصوير بالرنين المغناطيسي الوظيفي
EEG
مخطط كهربية الدماغ
EEG provides the recording of electrical activity of the brain from the surface of the scalp.
يوفر مخطط كهربية الدماغ تسجيل النشاط الكهربائي للدماغ من سطح فروة الرأس.
How does it work? Electrodes are placed on the scalp to pickup the electrical current generated by the brain.
كيف يعمل؟ يتم وضع أقطاب كهربائية على فروة الرأس لالتقاط التيار الكهربائي الذي يولده الدماغ.
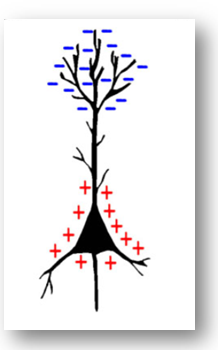
When firing, a neuron forms a dipole, with a lower voltage at synapses and higher voltage at the axon. If it’s an inhibitory neuron, the dipole is flipped, with lower voltage at axon and higher voltage at the synapses. What causes this voltage shift inside a neuron? Na+ channels open on along the dendrite, causing a flood of positive electrons, this positive charge moves down the axon, opening more sodium channels, and causing an electric charge to carry down the axon, discharging at the synapse, releasing neurotransmitters along with it. When groups of neurons fire together, they provide enough signal for us to measure from the scalp. We only able to measure clusters of neurons using EEG (about the size of a quarter in diameter).
عند إطلاق ، تشكل الخلية العصبية ثنائي القطب ، بجهد أقل عند المشابك والجهد العالي في المحور العصبي. إذا كانت خلية عصبية مثبطة ، ينقلب ثنائي القطب ، مع جهد أقل في محور عصبي وبجهد أعلى عند نقاط الاشتباك العصبي. ما الذي يسبب هذا التحول في الجهد داخل الخلايا العصبية؟ تنفتح قنوات Na + على طول التغصنات ، مما يتسبب في تدفق الإلكترونات الموجبة ، وتتحرك هذه الشحنة الموجبة لأسفل المحور العصبي ، وتفتح المزيد من قنوات الصوديوم ، وتتسبب في حمل شحنة كهربائية أسفل المحور العصبي ، وتفريغها عند المشبك ، وإطلاق النواقل العصبية معها. عندما تنطلق مجموعات من الخلايا العصبية معًا ، فإنها توفر لنا إشارة كافية للقياس من فروة الرأس. نحن قادرون فقط على قياس مجموعات الخلايا العصبية باستخدام مخطط كهربية الدماغ (حوالي ربع قطرها).
Advantages: it is portable, it can fit into a small suitcase (vs MEG which requires special built rooms). Lab grade EEG systems may be expensive, but they are cheaper than other BCI methods. In recent years an increasing number of commercial EEG systems have been released.
المزايا: إنها محمولة ، ويمكن وضعها في حقيبة صغيرة (مقابل MEG التي تتطلب غرفًا مبنية خاصة). قد تكون أنظمة EEG ذات التصنيف المعملية باهظة الثمن ، لكنها أرخص من طرق BCI الأخرى. في السنوات الأخيرة ، تم إصدار عدد متزايد من أنظمة EEG التجارية.
EEG data contains rhythmic activity, which reflects neural oscillations. Oscillations are described by frequency, power and phase. Oscillations occur at specific frequencies (i.e., at a certain rate). These include delta, theta, alpha, meta, and gamma. Research has found associations between these rhythms and different brain states. For example, commercial EEG headsets - often used for purposes such as meditation - typically measure the amount of brain activity that occurs in the alpha frequency.
تحتوي بيانات مخطط كهربية الدماغ على نشاط إيقاعي يعكس التذبذبات العصبية. يتم وصف التذبذبات بالتردد والقوة والمرحلة. تحدث التذبذبات عند ترددات محددة (أي بمعدل معين). وتشمل هذه دلتا ، ثيتا ، ألفا ، ميتا ، وجاما. وجد البحث ارتباطات بين هذه الإيقاعات وحالات الدماغ المختلفة. على سبيل المثال ، سماعات رأس EEG التجارية - غالبًا ما تستخدم لأغراض مثل التأمل - تقيس عادةً مقدار نشاط الدماغ الذي يحدث في تردد ألفا.
Spatial resolution
الدقة المكاني
The spatial resolution of EEG is determined by the number of electrodes used. In research, when higher spatial resolution is desired, typically at least 32 electrodes are used, up to 256. In general, spatial resolution for EEG is low (e.g., compared to ECoG and fMRI) because the signal needs to travel through different layers up to the skull. The resolution, however, can be improved using certain types of filters or by combining EEG with other tools (e.g., fMRI). (image of the electrodes placement..)
يتم تحديد الدقة المكانية لـ EEG من خلال عدد الأقطاب الكهربائية المستخدمة. في البحث ، عندما يكون مطلوب دقة مكانية أعلى ، يتم استخدام ما لا يقل عن 32 قطبًا كهربائيًا على الأقل ، حتى 256. بشكل عام ، تكون الدقة المكانية لـ EEG منخفضة (على سبيل المثال ، مقارنة بـ ECoG و fMRI) لأن الإشارة تحتاج إلى الانتقال عبر طبقات مختلفة للأعلى على الجمجمة. ومع ذلك ، يمكن تحسين الدقة باستخدام أنواع معينة من المرشحات أو عن طريق الجمع بين EEG والأدوات الأخرى (على سبيل المثال ، fMRI). (صورة وضع الأقطاب الكهربائية ..)
More electrodes cost more in time (e.g., setup), bandwidth (for data collection and analysis), and money (for material). Commercial headsets often use fewer electrodes because high spatial resolution (i.e., localizing the precise brain regions generating a signal) is not necessarily needed.
المزيد من الأقطاب الكهربائية تكلف أكثر في الوقت المناسب (على سبيل المثال ، الإعداد) ، وعرض النطاق الترددي (لجمع البيانات وتحليلها) ، والمال (للمواد). غالبًا ما تستخدم سماعات الرأس التجارية عددًا أقل من الأقطاب الكهربائية لأن الدقة المكانية العالية (أي تحديد مناطق الدماغ الدقيقة التي تولد إشارة) ليست ضرورية بالضرورة.
“The spatial precision of EEG is fairly low but can be improved by spatial filters such as the surface Laplacian or adaptive source-space-imaging techniques”
"الدقة المكانية لـ EEG منخفضة إلى حد ما ولكن يمكن تحسينها بواسطة المرشحات المكانية مثل Laplacian السطحي أو تقنيات التصوير المكاني للمصدر والفضاء"
Also spatial accuracy is low, because the activity registered by an electrode is the mixture of different signals generated by different brain regions, close and distant from the one placed under the electrode. Microscopic scale (less than a few cubic millimeters) = invisible to EEG, potentials are not powerful enough to reach the scalp. Mesoscopic scale (patches of cortex of several cubic millimeters to a few cubic centimeters) = can be detected with EEG but using more than 64 electrodes and spatial filtering techniques. Macroscopic scale (large region of cortex of many cubic centimeters) = easily measurable with EEG
كما أن الدقة المكانية منخفضة ، لأن النشاط المسجل بواسطة القطب الكهربي هو مزيج من الإشارات المختلفة التي تولدها مناطق الدماغ المختلفة ، القريبة والبعيدة عن تلك الموضوعة تحت القطب. المقياس المجهري (أقل من بضعة ملليمترات مكعبة) = غير مرئي لـ EEG ، الإمكانات ليست قوية بما يكفي للوصول إلى فروة الرأس. مقياس الميزوسكوب (بقع من القشرة من عدة مليمترات مكعبة إلى بضعة سنتيمترات مكعبة) = يمكن اكتشافه باستخدام EEG ولكن باستخدام أكثر من 64 قطبًا كهربائيًا وتقنيات التصفية المكانية. المقياس العياني (منطقة كبيرة من القشرة للعديد من السنتيمترات المكعبة) = يمكن قياسها بسهولة باستخدام مخطط كهربية الدماغ
Time resolution
دقة الوقت
EEG benefit is its excellent time resolution. It is possible to take thousand of snapshots of electrical activity across different sensors in a single second. In EEG is possible to use multiple electrodes, up to 500, based on the experiment. They are used mounted on caps to allow collecting the data from the same scalp region.
فائدة EEG هي دقة الوقت الممتازة. من الممكن التقاط آلاف اللقطات للنشاط الكهربائي عبر مستشعرات مختلفة في ثانية واحدة. في مخطط كهربية الدماغ من الممكن استخدام أقطاب متعددة ، حتى 500 ، بناءً على التجربة. يتم استخدامها مثبتة على أغطية للسماح بجمع البيانات من نفس منطقة فروة الرأس.
Comparison
مقارنة
BCI can use any type of brain imaging. These include fMRI, PET, and NIRS, which rely on changes in blood flow (i.e., hemodynamic response), and MEG and EEG, which measure the brain’s magnetic and electrical activity, respectively. While the spatial resolution of fMRI and NIRS are high, they have poor temporal resolution; MEG and PET have high spatial and temporal resolution; EEG has low spatial but high temporal resolution. Currently, fMRI and MEG rely on expensive, bulky equipment; PET requires the injection of a radioactive substance into the bloodstream. Thus, methods relying on NIRS and, in particular, EEG, are most commonly used.
يمكن لـ BCI استخدام أي نوع من أنواع تصوير الدماغ. وتشمل هذه التصوير بالرنين المغناطيسي الوظيفي ، و PET ، و NIRS ، والتي تعتمد على التغيرات في تدفق الدم (أي الاستجابة الديناميكية الدموية) ، و MEG و EEG ، والتي تقيس النشاط المغناطيسي والكهربائي للدماغ ، على التوالي. في حين أن الدقة المكانية للرنين المغناطيسي الوظيفي و NIRS عالية ، إلا أن الدقة الزمنية ضعيفة ؛ تتمتع MEG و PET باستبانة مكانية وزمنية عالية ؛ يحتوي EEG على دقة مكانية منخفضة ولكن زمنية عالية. يعتمد التصوير بالرنين المغناطيسي الوظيفي و MEG حاليًا على معدات ضخمة باهظة الثمن ؛ يتطلب PET حقن مادة مشعة في مجرى الدم. وبالتالي ، فإن الأساليب التي تعتمد على NIRS ، وعلى وجه الخصوص ، EEG ، هي الأكثر استخدامًا.
Components
عناصر
Brain activity
نشاط المخ
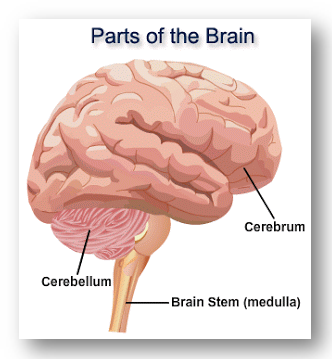
The nervous system is composed by two main parts: the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. The brain is the main organ of the central nervous system and it contains about 100 billions of neurons and trillions of cells called glia. The brain is composed by three major parts: the cerebrum (or cortex), the cerebellum (or little brain) and the brain stem.
يتكون الجهاز العصبي من جزأين رئيسيين: الجهاز العصبي المركزي والجهاز العصبي المحيطي. الدماغ هو العضو الرئيسي في الجهاز العصبي المركزي ويحتوي على حوالي 100 مليار من الخلايا العصبية وتريليونات الخلايا تسمى الخلايا الدبقية. يتكون الدماغ من ثلاثة أجزاء رئيسية: المخ (أو القشرة) والمخيخ (أو الدماغ الصغير) وجذع الدماغ.
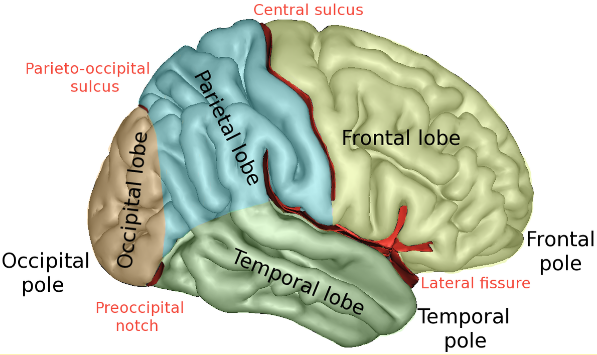
The cerebral cortex (or cerebrum) is divided into four main sections called lobes: Frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe and occipital lobe.
تنقسم القشرة الدماغية (أو المخ) إلى أربعة أقسام رئيسية تسمى الفصوص: الفص الجبهي والفص الجداري والفص الصدغي والفص القذالي.
The brain is constantly generating electric signals. The skull and skin of the head are very good electrical insulators though, making difficult to record from individual neurons. But when a big number of neurons do the same thing at the same time, it is possible to see the activity with electrodes placed on the surface of the scalp.
يولد الدماغ باستمرار إشارات كهربائية. تعتبر الجمجمة وجلد الرأس من العوازل الكهربائية الجيدة جدًا ، مما يجعل من الصعب تسجيلها من الخلايا العصبية الفردية. ولكن عندما يقوم عدد كبير من الخلايا العصبية بعمل نفس الشيء في نفس الوقت ، فمن الممكن رؤية النشاط باستخدام أقطاب كهربائية موضوعة على سطح فروة الرأس.
Nerve cells -> respond to stimuli and transmit information over long distances
Are composed by:
Axons -> long cylinder which transmits an electrical impulse and can be several meters long in vertebrates. In humans from a percentage of a millimetre to more than a metre. Axonal transport system for delivering proteins
Dendrites -> are connected to axons or dendrites of other cells - receives impulses from other nerves or relay the signals to other nerves.
Cell bodies -> single nucleus and contains most of the nerve cell metabolism
Glia cells - Located between neurons
الخلايا العصبية -> تستجيب للمنبهات وتنقل المعلومات عبر مسافات طويلة
تتكون من:
محاور -> أسطوانة طويلة تنقل نبضة كهربائية ويمكن أن يصل طولها إلى عدة أمتار في الفقاريات. في البشر من نسبة مليمتر إلى أكثر من متر. نظام النقل المحوري لتوصيل البروتينات
التشعبات -> متصلة بمحاور أو تشعبات لخلايا أخرى - تستقبل نبضات من أعصاب أخرى أو تنقل الإشارات إلى أعصاب أخرى. أجسام الخلايا -> نواة واحدة وتحتوي على معظم استقلاب الخلايا العصبية
الخلايا الدبقية - تقع بين الخلايا العصبية
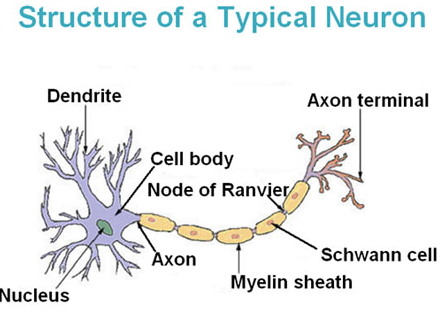
In the human brain, each nerve is connected to approximately 10 000 other nerves, mostly through dendritic connections. (21)
في الدماغ البشري ، كل عصب متصل بما يقرب من 10000 عصب آخر ، في الغالب من خلال وصلات شجيري. (21)
When the neurons communicate, currents occurs: an electrical signal is transmitted along an axon or a dendrite. The electrical signal at the end of the axon is converted into a chemical signal and the axon releases chemical messengers called neurotransmitters. The neurotransmitters travel through the synapse to the dendrite and are converted back to electrical signals.
عندما تتواصل الخلايا العصبية ، تحدث التيارات: يتم إرسال إشارة كهربائية على طول محور عصبي أو تغصن. يتم تحويل الإشارة الكهربائية في نهاية المحور العصبي إلى إشارة كيميائية ويطلق المحور العصبي رسلًا كيميائيًا يسمى الناقلات العصبية. تنتقل الناقلات العصبية عبر المشبك إلى التغصنات ويتم تحويلها مرة أخرى إلى إشارات كهربائية.
Where a current is leaving, there is a positive polarity, where a current is entering a negative polarity. These currents, called primary currents, are embedded in the brain tissue and brain liquor and reach the skull and scalp. The voltage differences at the scalp can be picked up by EEG electrodes. The main signals generating in the EEG are voltage gradients along dendrites in the upper cortical layers. To have a measurable signal, thousands of parallely oriented neighbouring dendrites have to be active synchronously. (22) The signals possible to measure through EEG are:
عندما يغادر التيار ، هناك قطبية موجبة ، حيث يدخل التيار في قطبية سالبة. هذه التيارات ، التي تسمى التيارات الأولية ، مغروسة في أنسجة المخ وسوائل المخ وتصل إلى الجمجمة وفروة الرأس. يمكن التقاط فروق الجهد في فروة الرأس بواسطة أقطاب تخطيط كهربية الدماغ. الإشارات الرئيسية المولدة في مخطط كهربية الدماغ هي تدرجات الجهد على طول التشعبات في الطبقات القشرية العليا. للحصول على إشارة قابلة للقياس ، يجب أن تكون آلاف التشعبات المجاورة ذات التوجه المتوازي نشطة بشكل متزامن. (22) الإشارات التي يمكن قياسها من خلال EEG هي:
1) Action potentials along the axons connecting neurons
2) currents through the synaptic clefts connecting axons with neurons/dendrites
3) currents along dendrites from synapses to the soma of neurons (23)
1) إمكانات العمل على طول المحاور التي تربط الخلايا العصبية
2) التيارات من خلال الشقوق المشبكية التي تربط المحاور العصبية بالخلايا العصبية / التشعبات
3) التيارات على طول التشعبات من نقاط الاشتباك العصبي إلى سوما من الخلايا العصبية (23)
Signal acquisition
اكتساب الإشارة
In the case of EEG-BCI, the electric potential of the brain activity is measured through electrodes placed on the scalp. Electrodes are metal discs placed on the scap in positions measured using the International 10/20 system.
في حالة تخطيط الدماغ الكهربائي EEG-BCI ، يتم قياس الجهد الكهربائي لنشاط الدماغ من خلال أقطاب كهربائية موضوعة على فروة الرأس. الأقطاب الكهربائية عبارة عن أقراص معدنية موضوعة على اللوح الخشبي في مواضع تم قياسها باستخدام نظام 10/20 الدولي.
There are two main types of electrodes:
هناك نوعان رئيسيان من الأقطاب الكهربائية:
Wet - using saline solution of gel. Conductivity is increased because the electrical distance is minimized. The majority are made of stainless steel, tin, gold or silver and which are covered with a silver chloride coating.
رطب - باستخدام محلول ملحي من الجل. يتم زيادة الموصلية نظرًا لتقليل المسافة الكهربائية. معظمها مصنوع من الفولاذ المقاوم للصدأ أو القصدير أو الذهب أو الفضة وهي مغطاة بطبقة من كلوريد الفضة.

Dry - more convenient and easier to use, but can lose higher frequencies Photo - more info
جاف - أكثر ملاءمة وأسهل في الاستخدام ، لكن يمكن أن يفقد ترددات أعلى صور - مزيد من المعلومات
To help the position, as many electrodes are required -> cap
EEG is reliable for real-time applications as it can take measurements every thousandths of a second. EEG problem is noise. Being the electrodes placed on the scalp, there are layers in between, plus background noise and muscles.
للمساعدة في هذا الموقف ، حيث أن العديد من الأقطاب الكهربائية مطلوبة -> غطاء
يعتبر مخطط كهربية الدماغ (EEG) موثوقًا للتطبيقات في الوقت الفعلي حيث يمكنه إجراء قياسات كل جزء من الألف من الثانية. مشكلة مخطط كهربية الدماغ هي الضوضاء. يجري وضع الأقطاب الكهربائية على فروة الرأس ، وهناك طبقات بينهما ، بالإضافة إلى ضوضاء الخلفية والعضلات.
HOW EEG ACQUISITION WORKS?
كيف يتم الحصول على مخطط كهربية الدماغ؟
EEG measures the electric activity happening in the brain. What is recorded is the voltage difference between minimum 2 electrodes. The EEG needs to be recorded simultaneously from multiple electrodes, in order to interpret ERP. During synaptic excitation of the dendrites in the neurons, electric currents are generated and picked up by the EEG. Because the signal detected is poor, being the electrodes far from the neurons and having the signal to travel through bones and skull, to record the electric flow is then required an amplifier.
يقيس مخطط كهربية الدماغ (EEG) النشاط الكهربائي الذي يحدث في الدماغ. ما يتم تسجيله هو فرق الجهد بين قطبين كحد أدنى. يجب تسجيل مخطط كهربية الدماغ في وقت واحد من عدة أقطاب كهربائية ، من أجل تفسير تخطيط موارد المؤسسات. أثناء الإثارة المتشابكة للتشعبات في الخلايا العصبية ، يتم توليد التيارات الكهربائية والتقاطها بواسطة مخطط كهربية الدماغ. نظرًا لضعف الإشارة المكتشفة ، نظرًا لكون الأقطاب الكهربائية بعيدة عن الخلايا العصبية ولديها إشارة للتنقل عبر العظام والجمجمة ، فإن تسجيل التدفق الكهربائي يتطلب مضخمًا.
What is needed?
Electrodes - usually made of silver chloride
Amplifiers
A/D converters
Recording Device
ما المطلوب؟
الأقطاب الكهربائية - عادة ما تكون مصنوعة من كلوريد الفضة
مكبرات الصوت
محولات A / D
جهاز تسجيل
“The electrodes acquire the signal from the scalp, the amplifiers process the analog signal to enlarge the amplitude of the EEG signals so that the A/D converter can digitalize the signal in a more accurate way. Finally, the recording device, which may be a personal computer or similar, stores, and displays the data.” (24)
"تحصل الأقطاب الكهربائية على الإشارة من فروة الرأس ، وتعالج مكبرات الصوت الإشارة التناظرية لتكبير اتساع إشارات مخطط كهربية الدماغ بحيث يمكن لمحول A / D تحويل الإشارة رقميًا بطريقة أكثر دقة. أخيرًا ، يقوم جهاز التسجيل ، الذي قد يكون جهاز كمبيوتر شخصي أو ما شابه ، بتخزين البيانات وعرضها ". (24)
Electrodes
أقطاب كهربائية
As previously introduced, different types of electrodes are available to use in EEG, such as: disposable (dry or wet), reusable disc electrodes (gold, silver, stainless steel or tin), headbands and electrodes caps (such as the consumer ones), saline-based electrodes, needle electrodes (25) . In the 1958 a standard system of electrodes placement had been developed, where the head is divided in proportional distances (Jasper, 1958).
كما تم تقديمه سابقًا ، تتوفر أنواع مختلفة من الأقطاب الكهربائية للاستخدام في مخطط كهربية الدماغ ، مثل: أقطاب كهربائية يمكن التخلص منها (جافة أو رطبة) ، وأقطاب قرصية قابلة لإعادة الاستخدام (ذهبية ، أو فضية ، أو فولاذ مقاوم للصدأ أو قصدير) ، وأربطة رأس وأغطية أقطاب كهربائية (مثل المستهلكات) ، أقطاب كهربائية ذات قاعدة ملحية ، أقطاب إبرة (25). في عام 1958 ، تم تطوير نظام قياسي لوضع الأقطاب الكهربائية ، حيث يتم تقسيم الرأس إلى مسافات متناسبة (جاسبر ، 1958).
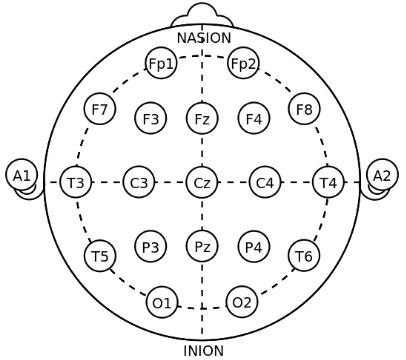
locations of International 10-20 system for EEG (electroencephalography) recording (26)
The minimal configuration is composed by three electrodes: active electrode, reference electrode and ground electrode. The EEG measures the potential difference over time between signal or active electrode and the reference electrode. It is very difficult to get a reference where no electrical activity from the brain is present. Usually it is located on the mastoid, ear lobes or tip of the nose. The ground electrode is used to measure the differential voltage between the active and the reference points.
مواقع النظام الدولي 10-20 لتسجيل EEG (تخطيط كهربية الدماغ) (26)
يتكون الحد الأدنى من التكوين من ثلاثة أقطاب: قطب كهربائي نشط وقطب مرجعي وقطب أرضي. يقيس مخطط كهربية الدماغ فرق الجهد بمرور الوقت بين الإشارة أو القطب النشط والقطب المرجعي. من الصعب جدًا الحصول على مرجع في حالة عدم وجود نشاط كهربائي من الدماغ. عادة ما يكون موجودًا على الخشاء أو شحمة الأذن أو طرف الأنف. يستخدم القطب الأرضي لقياس الجهد التفاضلي بين النقطتين النشطة والمرجعية.
Amplifier
المضخم
The signal picked up by the electrodes is far away and attenuated by the different layers it has to travel. For this reason an amplifier is needed to bring the microvolts to a range that can be digitized. The signal is sent to an amplifier through a cable measuring 1-2 metres. Unfortunately the cables can act as antenna and pickup signals, which would interfere with the EEG signal and cause noise to be amplified. Some “active” electrodes include a small pre-amplifier within the electrode, to avoid this noise interference. Unfortunately they are quite large and expensive and might not be appropriate in some situations. (27)
تكون الإشارة التي تلتقطها الأقطاب الكهربائية بعيدة ويتم إضعافها بواسطة الطبقات المختلفة التي يجب أن تنتقل إليها. لهذا السبب ، هناك حاجة إلى مكبر للصوت للوصول بالفولتات الدقيقة إلى نطاق يمكن رقمنته. يتم إرسال الإشارة إلى مكبر الصوت من خلال كابل يبلغ قياسه 1-2 متر. لسوء الحظ ، يمكن أن تعمل الكابلات كإشارات هوائي وإشارات التقاط ، مما قد يتداخل مع إشارة EEG ويسبب تضخيم الضوضاء. تتضمن بعض الأقطاب "النشطة" مضخمًا أوليًا صغيرًا داخل القطب لتجنب تداخل الضوضاء. لسوء الحظ ، فهي كبيرة جدًا ومكلفة وقد لا تكون مناسبة في بعض المواقف. (27)
A/D converters
محولات A / D
The A/D converter will convert the amplified signal from analog to digital form. The bandwidth for EEG signals is limited to approximately 100Hz, making 200Hz enough for sampling EEG signals.
يقوم محول A / D بتحويل الإشارة المضخمة من الشكل التناظري إلى الشكل الرقمي. يقتصر عرض النطاق الترددي لإشارات EEG على 100 هرتز تقريبًا ، مما يجعل 200 هرتز كافية لأخذ عينات إشارات EEG.
Recording device
جهاز تسجيل
It can be a computer or similar device, which will record, store and display the converted signal.
يمكن أن يكون جهاز كمبيوتر أو جهازًا مشابهًا ، والذي سيقوم بتسجيل وتخزين وعرض الإشارة المحولة.
Preprocessing
المعالجة
The raw EEG data is often not clean because affected by noise and artifacts. There are four main sources of noise and artifacts, which are:
غالبًا ما تكون بيانات EEG الأولية غير نظيفة لأنها تتأثر بالضوضاء والتحف. هناك أربعة مصادر رئيسية للضوضاء ، وهي:
EEG equipment
Electrical interference external to the subject and recording system
The leads and electrodes
The subject: electrical activity from the heart, eye blinking, eyeball movements, muscles movements in general. (29)
معدات EEG
تداخل كهربائي خارجي ونظام التسجيل
الخيوط والأقطاب
الشخص: نشاط كهربائي من القلب ، وميض العين ، وحركات مقلة العين ، وحركات العضلات بشكل عام. (29)
Eye blinking are very clear in frontal and occipital recordings, while ECGs (from the heart electrical activity) on the occipital electrodes. “A movement of the eyeball and the eyelids causes a change in the potential field because of the existing potential difference of about 100mV between the cornea and the retina” (30)
وميض العين واضح جدًا في التسجيلات الأمامية والقذالية ، بينما يكون رسم القلب الكهربائي (من النشاط الكهربائي للقلب) على الأقطاب القذالية. "حركة مقلة العين والجفون تسبب تغيرًا في المجال المحتمل بسبب فرق الجهد الحالي البالغ حوالي 100 مللي فولت بين القرنية والشبكية" (30)
The preprocessing step helps to clean the data from the noise and artifacts. There are different methods and different steps in preprocessing. Often for example, filters are applied to the data. To remove the DC components of the signal and the drifts are employed high-pass filters, where usually a frequency cut-off of 1Hz is enough. Often also low pass filters can be applied to remove the high frequencies of the signal, because in EEG usually frequencies over 90Hz are not studied. Other methods are used to remove artefacts as the eyeball movements or eye blinking.
تساعد خطوة المعالجة المسبقة على تنظيف البيانات من الضوضاء والتحف. هناك طرق مختلفة وخطوات مختلفة في المعالجة المسبقة. غالبًا على سبيل المثال ، يتم تطبيق عوامل التصفية على البيانات. لإزالة مكونات التيار المستمر للإشارة ، يتم استخدام المرشحات عالية التمرير ، حيث عادةً ما يكون قطع التردد 1 هرتز كافياً. غالبًا ما يمكن أيضًا تطبيق مرشحات تمرير منخفض لإزالة الترددات العالية للإشارة ، لأنه في EEG عادةً لا يتم دراسة الترددات التي تزيد عن 90 هرتز. يتم استخدام طرق أخرى لإزالة القطع الأثرية مثل حركات مقلة العين أو وميض العين.
After different steps of pre-processing, when the signal is clean from most of the artifacts and noise, the recording is cut in epoch of few seconds: this allows us to have a large number of features from a single EEG recording, and to use them for statistics or to apply classifiers, as we will see in the next sections. (31)
بعد خطوات مختلفة من المعالجة المسبقة ، عندما تكون الإشارة نظيفة من معظم القطع الأثرية والضوضاء ، يتم قطع التسجيل في فترة ثوانٍ قليلة: وهذا يسمح لنا بالحصول على عدد كبير من الميزات من تسجيل EEG واحد ، واستخدام عليها للإحصاءات أو لتطبيق المصنفات ، كما سنرى في الأقسام التالية. (31)
Feature Extraction
الميزات استخراج
The next step is feature extraction: the analysis of the signal and extraction of information. As the EEG signal is very complex, it is impossible to find meaningful information just looking at it. It is needed then to apply processing algorithms which allows to find content (such as a person’s intent, for example) which would be hidden at a naked eye. There are many methods for feature extraction, some of them are: Band powers (BP) Cross-correlation between EEG band powers frequency representation (FR) time-frequency representation (TFR) Hjorth parameters, parametric modelling inverse model and specific techniques used for P300 and VEP such as Peak picking (PP) and Slow cortical potentials calculation (SCPs) (32)
الخطوة التالية هي استخراج الميزة: تحليل الإشارة واستخراج المعلومات. نظرًا لأن إشارة EEG معقدة للغاية ، فمن المستحيل العثور على معلومات مفيدة بمجرد النظر إليها. من الضروري بعد ذلك تطبيق خوارزميات المعالجة التي تسمح بالعثور على المحتوى (مثل نية الشخص ، على سبيل المثال) والذي سيكون مخفيًا بالعين المجردة. هناك العديد من الطرق لاستخراج الميزات ، بعضها: قوى النطاق (BP) الارتباط المتبادل بين قوى النطاق EEG تمثيل التردد (FR) تمثيل التردد الزمني (TFR) معلمات Hjorth ، النموذج العكسي للنمذجة البارامترية والتقنيات المحددة المستخدمة في P300 و VEP مثل انتقاء الذروة (PP) وحساب الجهود القشرية البطيئة (SCPs) (32)
Classification
تصنيف
Another step which can be applied to the signal, now mostly clean from artifacts, is to apply classification algorithms. Using machine learning techniques it is possible to train a classifier to recognize which features, for example, belongs to one or another class.mathematical Again, the classification helps to find out which kind of mental task the subject is performing (Ochoa, 2002)
الخطوة الأخرى التي يمكن تطبيقها على الإشارة ، والتي أصبحت الآن نظيفة في الغالب من القطع الأثرية ، هي تطبيق خوارزميات التصنيف. باستخدام تقنيات التعلم الآلي ، من الممكن تدريب المصنف على التعرف على الميزات ، على سبيل المثال ، التي تنتمي إلى فئة واحدة أو أخرى.
Translation
ترجمة
After the signal has been classified, the result is passed to the feature translation algorithm. At this point the features need to be translated in the corresponding action required. “For example, a P3 potential could be translated into the selection of the letter that evoked it” So, in this case, the algorithm will send a command to the feedback device, to select the letter.
بعد تصنيف الإشارة ، يتم تمرير النتيجة إلى خوارزمية ترجمة الميزة. في هذه المرحلة ، يجب ترجمة الميزات في الإجراء المقابل المطلوب. "على سبيل المثال ، يمكن ترجمة إمكانية P3 إلى اختيار الحرف الذي أثارها" لذا ، في هذه الحالة ، سترسل الخوارزمية أمرًا إلى جهاز التغذية الراجعة ، لتحديد الحرف.
Feedback device
جهاز الملاحظات
The feedback device receives the command from the translation step. For example it can be the computer, where the signal will be used to move a cursor, or it could be a robotic arm where the data are used to allow movement.
يتلقى جهاز الملاحظات الأمر من خطوة الترجمة. على سبيل المثال ، يمكن أن يكون الحاسوب ، حيث سيتم استخدام الإشارة لتحريك المؤشر ، أو يمكن أن يكون ذراعًا آليًا حيث تُستخدم البيانات للسماح بالحركة
Limitations
محددات
The current status of BCI has still many limitations to be overcome: Hardware / Software The first problem is the signal acquisition hardware. Regarding EEG, the sensors still have acquisition limits. As we have seen, the signal travels distance before being acquired by the EEG machine, and the noise and artefacts are causing important problems. EEG must achieve a good performance in all environments. Reliable electrodes are necessary. The technology must be able to be reliable despite the noise generated by devices, as many BCI are targeted to ill patients, which are often surrounded by many electronic equipments. (33) The best signal we have seen is the one acquired through invasive technology. But the invasive BCIs suffer as well of many limitations. First of all they are implanted only in a small amount of patients which requires surgery for other reasons. There are ethical issues involved with invasive technology (? check ethical section ?). The problems to overcome are complex: the system need to be safe and remain intact, functional and reliable for decades. The safety long term must be demonstrated, as the implant could potentially open the way to infections or be rejected by the body. The implant must have external elements that are robust, comfortable, convenient, and unobtrusive; and interfaces easily with high-performance applications. And safe. (34) When used to study the brain, invasive technology might not have the best models, being implanted in patients with problems or injuries which does not make them the ideal candidates. BCI validation and dissemination Reliability (35)
لا يزال للوضع الحالي لـ (همس) العديد من القيود التي يجب التغلب عليها: الأجهزة / البرامج المشكلة الأولى هي أجهزة الحصول على الإشارة. فيما يتعلق بالتخطيط الكهربائي للدماغ ، لا تزال أجهزة الاستشعار لها حدود اكتساب. كما رأينا ، تنتقل الإشارة مسافة قبل أن يتم الحصول عليها بواسطة جهاز مخطط كهربية الدماغ ، وتسبب الضوضاء والمصنوعات اليدوية مشاكل مهمة. يجب أن يحقق مخطط كهربية الدماغ أداءً جيدًا في جميع البيئات. الأقطاب الكهربائية الموثوقة ضرورية. يجب أن تكون التقنية قادرة على أن تكون موثوقة على الرغم من الضوضاء الناتجة عن الأجهزة ، حيث أن العديد من BCI تستهدف المرضى المرضى ، والذين غالبًا ما يكونون محاطين بالعديد من المعدات الإلكترونية. (33) أفضل إشارة رأيناها هي تلك التي تم الحصول عليها من خلال التكنولوجيا الغازية. لكن (همس) الغازية تعاني أيضًا من العديد من القيود. بادئ ذي بدء ، يتم زرعها فقط في عدد قليل من المرضى مما يتطلب جراحة لأسباب أخرى. هناك قضايا أخلاقية مرتبطة بالتكنولوجيا الغازية (؟ تحقق من القسم الأخلاقي؟). المشاكل التي يجب التغلب عليها معقدة: يجب أن يكون النظام آمنًا وأن يظل سليمًا وفعالًا وموثوقًا به لعقود. يجب إثبات الأمان على المدى الطويل ، حيث من المحتمل أن تفتح الغرسة الطريق للعدوى أو أن يرفضها الجسم. يجب أن تحتوي الغرسة على عناصر خارجية قوية ومريحة ومريحة وغير مزعجة ؛ وواجهات سهلة مع التطبيقات عالية الأداء. و أمن. (34) عند استخدامها لدراسة الدماغ ، قد لا تحتوي التكنولوجيا الغازية على أفضل النماذج ، حيث يتم زرعها في المرضى الذين يعانون من مشاكل أو إصابات لا تجعلهم المرشحين المثاليين. موثوقية التحقق من صحة (همس) ونشرها (35)
Current understanding of biological signals and Variability
الفهم الحالي للإشارات البيولوجية والتقلبات
The problem is that is difficult to decode the signal or it requires months of training and it’s different for each person - not standard. The variability of signal features causes a need for adaptive BCI algorithms for proper function; Despite the known basic rules of BCIs’ selection and adjustment, it is still unclear why some BCI paradigms or features are effective with some patients, and some not. Research on so called “BCI demographic assessment”, i. e. how many people and which people may use a particular kind of BCI, was partly (in the area of steady-state visual evoked potentials – SSVEP-based BCI) provided by Allison et al. (Allison et al., 2010) and Volosyak et al. (36)
تكمن المشكلة في صعوبة فك تشفير الإشارة أو أنها تتطلب شهورًا من التدريب وتختلف من شخص لآخر - وليست قياسية. يؤدي تغير ميزات الإشارة إلى الحاجة إلى خوارزميات (همس) التكيفية للوظيفة المناسبة ؛ على الرغم من القواعد الأساسية المعروفة لاختيار وتعديل (همس) ، لا يزال من غير الواضح سبب فعالية بعض نماذج أو ميزات (همس) مع بعض المرضى ، والبعض الآخر لا. بحث حول ما يسمى "التقييم الديموغرافي (همس)" ، ط. ه. كم عدد الأشخاص وأي أشخاص قد يستخدمون نوعًا معينًا من (همس) ، كان جزئيًا (في مجال الإمكانات المرئية المستثارة ذات الحالة المستقرة - (همس) المستندة إلى SSVEP) التي قدمها أليسون وآخرون. (أليسون وآخرون ، 2010) وفولوسياك وآخرون. (36)
Ethics
أخلاق مهنية
Emerging technologies and brain computer interfaces raise many ethical concerns that are being addressed by the neuroscience community. The problems touch different topics, such as managing patient expectations, the concept of personal identity, and the validity of informed consent and so on.
Informed consent One important ethical issue related to medical application of BCI, is around getting an informed consent from the patients. Often BCI research is carried out with patients affected by debilitating issues, such as locked in syndrome or different degree of strokes. It is important to recognize if the consent obtained is fully informed or affected by the disability.
Setting patients expectations W. Glannon highlighted how patients and their relatives might have expectations surrounding BMI technologies that might not be met. Different reasons might affect the ability or not of BCI to work, such as cognitive capacity or level of disability of the subject. The risk of the technology not working could cause significant distress to the patients, outweighing the possible benefits.
Risks vs benefits Some specific technologies, such as implantable devices, might pose risks for the patient health. It is an important ethical problem to address/
Privacy The theory of being able to read minds, have a profound impact on the concept of personal identity and privacy. Even if the technology is still far from being able to read the thoughts of a person, it is important to start considering the ethical implications. If such a machine will be developed, how the data will be transmitted and stored? How the person could keep full ownership and avoid hackers or other person accessing “his thoughts”?
Legal Implications Brain computer interface is often used with paralyzed people to help them in re-gain movements using prosthetic limbs. Some researchers questioned who would have the responsibility in case an accident happened using such methods. How would be possible to distinguish a voluntary action from a malfunction of the system? In addition, the ability to make communicate seriously ill patients might raise the question if their answers can be considered an informed consent given their status.
Impact on society Considering the possibility of BCI to increase mental ability, joining with Artificial Intelligence (as for example in Elon Musk plan). We question ourselves if athletes with prosthetic limbs should compete with the others, at the same time if the BCI improves cognition, we would have a similar issue.
تثير التقنيات الناشئة وواجهات الحاسوب في الدماغ العديد من المخاوف الأخلاقية التي يعالجها مجتمع علم الأعصاب. تمس المشاكل مواضيع مختلفة ، مثل إدارة توقعات المريض ، ومفهوم الهوية الشخصية ، وصحة الموافقة المستنيرة وما إلى ذلك.
الموافقة المستنيرة تتمثل إحدى القضايا الأخلاقية المهمة المتعلقة بالتطبيق الطبي ل(همس) في الحصول على موافقة مستنيرة من المرضى. غالبًا ما يتم إجراء أبحاث (همس) مع مرضى يعانون من مشاكل موهنة ، مثل متلازمة الانغلاق أو درجات مختلفة من السكتات الدماغية. من المهم معرفة ما إذا كانت الموافقة التي تم الحصول عليها مستنيرة تمامًا أو متأثرة بالإعاقة.
تحديد توقعات المرضى سلط دبليو جلانون الضوء على الكيفية التي قد يكون لدى المرضى وأقاربهم توقعات حول تقنيات مؤشر كتلة الجسم التي قد لا تتحقق. قد تؤثر الأسباب المختلفة على قدرة أو عدم قدرة BCI على العمل ، مثل القدرة المعرفية أو مستوى الإعاقة للموضوع. قد يتسبب عدم نجاح التقنية في حدوث ضائقة كبيرة للمرضى ، مما يفوق الفوائد المحتملة.
المخاطر مقابل الفوائد قد تشكل بعض التقنيات المحددة ، مثل الأجهزة القابلة للزرع ، مخاطر على صحة المريض. إنها مشكلة أخلاقية مهمة يجب معالجتها /
الخصوصية إن نظرية القدرة على قراءة العقول لها تأثير عميق على مفهوم الهوية الشخصية والخصوصية. حتى لو كانت التكنولوجيا لا تزال بعيدة عن القدرة على قراءة أفكار الشخص ، فمن المهم البدء في التفكير في الآثار الأخلاقية. إذا تم تطوير مثل هذه الآلة ، فكيف سيتم نقل البيانات وتخزينها؟ كيف يمكن للشخص أن يحتفظ بالملكية الكاملة ويتجنب المتسللين أو أي شخص آخر الوصول إلى "أفكاره"؟
المقتضيات القانونية غالبًا ما تُستخدم واجهة الدماغ الحاسوبية مع الأشخاص المصابين بالشلل لمساعدتهم على استعادة حركاتهم باستخدام الأطراف الاصطناعية. وتساءل بعض الباحثين عن الجهة المسؤولة في حالة وقوع حادث باستخدام مثل هذه الأساليب. كيف يمكن التمييز بين عمل تطوعي وخلل في النظام؟ بالإضافة إلى ذلك ، فإن القدرة على التواصل مع المرضى المصابين بأمراض خطيرة قد تثير السؤال عما إذا كانت إجاباتهم يمكن اعتبارها موافقة مستنيرة بالنظر إلى حالتهم.
التأثير على المجتمع النظر في إمكانية BCI لزيادة القدرة العقلية ، والانضمام إلى الذكاء الاصطناعي (على سبيل المثال في خطة Elon Musk). نتساءل عما إذا كان يجب على الرياضيين ذوي الأطراف الاصطناعية التنافس مع الآخرين ، وفي نفس الوقت إذا حسنت BCI الإدراك ، فسنواجه مشكلة مماثلة.
Future of the field
مستقبل المجال
Neuroelectrical activity was detected first by Hans Berger in 1924 and recorded in EEG. In the 70s the Defence Advanced Research project Agency started to explore brain communication using EEGm, and in 1976 UCLA’s Brain Computer Interface Laboratory provided evidence that evoked potentials could be used to control a cursor. In the same year Jacques J. Vidal creates the term BCI. In the last 50 years the field had been evolving at a fast pace. Few important milestones:
1998: First (invasive, non-EEG) implant in the human brain that produces high quality signals
1999: BCI is used to aid a quadriplegic for limited hand movement
2002: Monkeys are trained to control a computer cursor
2003: First BCI game is demonstrated to the public (BrainGate)
2005: Monkey brain controls a robotic arm
2008: Voiceless phone calls are demonstrated (The Audeo – TI developers conference)
2014 Direct brain-to-brain communication achieved by transmitting EEG signals over the internet (37)
These advancements show that BCI is a dynamic and growing field. As it is a multidisciplinary field, the evolution is affected by different factors, as new hardware, new machine learning / mathematical theories, advancements in AI and robotics, new discoveries in medicine and neuroscience, etc etc In general the field of BCI has always been limited to the academic world or medical field. Recently new startups joined the study, seeking the enhancement of human capabilities: Facebook, Neuralink, Kernel.
Facebook started hiring Brain Computer Interface Engineers and neural imaging engineers in April 2017, to work on a 2 year B8 project using machine learning and neuroimaging. The plan is to use optical imaging for scanning the brain to detect the speaking in the head and translate it into text. Facebook’s goal is to allow people to type 100 words per minute, which is faster than typing on a phone (and could allow also to people which cannot type?). The following post appeared on Zuckeberg’s timeline:
تم اكتشاف النشاط الكهربائي العصبي لأول مرة بواسطة هانز بيرجر في عام 1924 وتم تسجيله في مخطط كهربية الدماغ. في السبعينيات من القرن الماضي ، بدأت وكالة مشروع الأبحاث الدفاعية المتقدمة في استكشاف اتصالات الدماغ باستخدام EEGm ، وفي عام 1976 قدم مختبر واجهة الدماغ الحاسوبي بجامعة كاليفورنيا في لوس أنجلوس دليلًا على أنه يمكن استخدام الإمكانات المستثارة للتحكم في المؤشر. في نفس العام أنشأ جاك ج. فيدال مصطلح BCI. في السنوات الخمسين الماضية كان المجال يتطور بوتيرة سريعة. بعض المعالم الهامة:
1998: أول غرسة (غازية غير EEG) في الدماغ البشري تنتج إشارات عالية الجودة
1999: تم استخدام BCI لمساعدة المصابين بالشلل الرباعي لحركة اليد المحدودة
2002: تم تدريب القرود على التحكم في مؤشر الحاسوب
2003: عرض أول لعبة BCI للجمهور (BrainGate)
2005: دماغ القرد يتحكم في ذراع آلية
2008: عرض المكالمات الهاتفية التي لا صوت لها (مؤتمر Audeo - TI Developers)
2014 التواصل المباشر من الدماغ إلى الدماغ الذي تم تحقيقه عن طريق إرسال إشارات EEG عبر الإنترنت (37)
تظهر هذه التطورات أن BCI هو مجال ديناميكي ومتزايد. نظرًا لأنه مجال متعدد التخصصات ، يتأثر التطور بعوامل مختلفة ، مثل الأجهزة الجديدة ، والتعلم الآلي الجديد / النظريات الرياضية ، والتطورات في الذكاء الاصطناعي والروبوتات ، والاكتشافات الجديدة في الطب وعلم الأعصاب ، إلخ. يقتصر على العالم الأكاديمي أو المجال الطبي. انضمت الشركات الناشئة الجديدة مؤخرًا إلى الدراسة ، سعياً وراء تعزيز القدرات البشرية: Facebook و Neuralink و Kernel.
فيسبوك
بدأ Facebook في التعاقد مع مهندسي Brain Computer Interface ومهندسي التصوير العصبي في أبريل 2017 ، للعمل في مشروع B8 لمدة عامين باستخدام التعلم الآلي والتصوير العصبي. تتمثل الخطة في استخدام التصوير البصري لمسح الدماغ لاكتشاف الكلام في الرأس وترجمته إلى نص. هدف Facebook هو السماح للأشخاص بكتابة 100 كلمة في الدقيقة ، وهو أسرع من الكتابة على الهاتف (ويمكن أن يسمح أيضًا للأشخاص الذين لا يستطيعون الكتابة؟). المنشور التالي ظهر في الجدول الزمني لزوكبيرج:
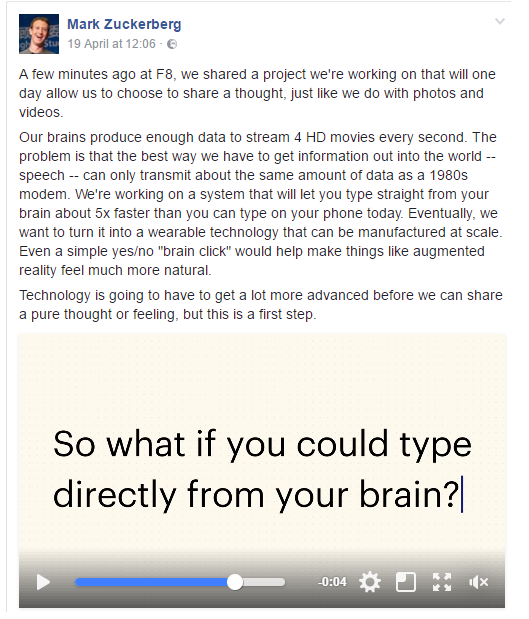
Facebook is collaborating with UC San Francisco, UC Berkeley, Johns Hopkins Medicine, Johns Hopkins University’s Applied Physics Laboratory and Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis on this project. It is building hardware and software to mimic the cochlea in the ear which translates sound in specific frequencies for the brain. In the tests performed they have been able to use a vocabulary of 9 words to be hard through the skin.
Neuralink
Elon Musk’s Neuralink was publicly launched in March 2017. The announcement was made the day after Facebook announced its BCI project. Elon Musk has referred few times to a “neural lace”, an AI layer which would augment human brain’s abilities. In a detailed report on the website Wait but why, they refer to it as a “Wizard Hat”. It would be a “third layer” which would complement the other two: the limbic system and the cortex. The main idea of its creator is to build implantable devices to help humans keeping up with the raise of Artificial intelligence. In the beginnings the implants could be used to study the brain and to help in treating disease as depression or epilepsy. Implantable electrodes would allow a much better quality than EEG, but the invasive technology raises many concerns. Implantable devices need to be safe, also in the long term, biocompatible have a wireless form of communication which would not degrade with time, the power problem need to be solved and Musk would needs to find volunteers for the experiments. Also Musk is talking about “one million simultaneously recorded neurons”, which is a huge number compared to the roughly maximum of 200 electrodes placed in current experiments. In a statement, the CEO of Neuralink said that “For a meaningful partial brain interface, I think we’re roughly four or five years away.”
Kernel
For Kernel as well the final goal is to allow humans to coexist and co-evolve with machines. Its founder, Bryan Johnson, invested $100 million to develop brain implants. The focus will be first on medical applications, trying to understand better the brain, to move in the future toward augmenting it to make human smarter and healthier. Kernel promised to improve neurodegenerative diseases, a big claim as so far, brain implants had been using only in paraplegic people and for medical trials. (38) They are developing hardware and software at the moment to treat people with Parkinsons disease and the company has at the moment about 20 employees.
يتعاون Facebook مع جامعة كاليفورنيا في سان فرانسيسكو وجامعة كاليفورنيا في بيركلي وجونز هوبكنز ميديسن ومختبر الفيزياء التطبيقية بجامعة جونز هوبكنز وكلية الطب بجامعة واشنطن في سانت لويس في هذا المشروع. تقوم ببناء أجهزة وبرامج لتقليد القوقعة في الأذن والتي تترجم الصوت بترددات محددة للدماغ. في الاختبارات التي تم إجراؤها ، تمكنوا من استخدام مفردات من 9 كلمات ليكونوا صعبًا على الجلد.
نيورالينك
تم إطلاق Neuralink من Elon Musk علنًا في مارس 2017. تم الإعلان بعد يوم من إعلان Facebook عن مشروع BCI. أشار Elon Musk عدة مرات إلى "الدانتيل العصبي" ، وهي طبقة ذكاء اصطناعي من شأنها زيادة قدرات الدماغ البشري. في تقرير مفصل على الموقع الإلكتروني "انتظر ولكن لماذا" ، يشيرون إليها على أنها "قبعة ساحر". ستكون "طبقة ثالثة" تكمل الطبقتين الأخريين: الجهاز الحوفي والقشرة. الفكرة الرئيسية لمنشئها هي بناء أجهزة قابلة للزرع لمساعدة البشر على مواكبة زيادة الذكاء الاصطناعي. في البداية ، كان من الممكن استخدام الغرسات لدراسة الدماغ وللمساعدة في علاج المرض مثل الاكتئاب أو الصرع. ستسمح الأقطاب الكهربائية المزروعة بجودة أفضل بكثير من EEG ، لكن التكنولوجيا الغازية تثير العديد من المخاوف. يجب أن تكون الأجهزة القابلة للزرع آمنة ، وعلى المدى الطويل أيضًا ، يجب أن يكون المتوافق حيويًا مع شكل لاسلكي من الاتصالات لن يتحلل بمرور الوقت ، ويجب حل مشكلة الطاقة وسيحتاج Musk إلى إيجاد متطوعين للتجارب. كما يتحدث ماسك عن "مليون خلية عصبية مسجلة في وقت واحد" ، وهو عدد ضخم مقارنة بالحد الأقصى البالغ 200 قطب كهربائي موضوعة في التجارب الحالية. في بيان ، قال الرئيس التنفيذي لشركة Neuralink: "للحصول على واجهة دماغية جزئية ذات مغزى ، أعتقد أننا ما زلنا على بعد أربع أو خمس سنوات تقريبًا."
Kernel
بالنسبة إلى Kernel أيضًا ، فإن الهدف النهائي هو السماح للبشر بالتعايش والتطور المشترك مع الآلات. استثمر مؤسسها ، برايان جونسون ، 100 مليون دولار لتطوير عمليات زرع الدماغ. سيكون التركيز أولاً على التطبيقات الطبية ، في محاولة لفهم الدماغ بشكل أفضل ، للتحرك في المستقبل نحو زيادته لجعل الإنسان أكثر ذكاءً وصحة. وعد Kernel بتحسين الأمراض التنكسية العصبية ، وهو ادعاء كبير حتى الآن ، كانت غرسات الدماغ تستخدم فقط في الأشخاص المصابين بشلل نصفي وللتجارب الطبية. (38) إنهم يطورون أجهزة وبرامج في الوقت الحالي لعلاج الأشخاص المصابين بمرض باركنسون ولديها في الوقت الحالي حوالي 20 موظفًا.